
This is the third installment in our 5-part “Investing In Nigeria” series. The first was on “Mutual Funds” and the next “Stock“. Here at Mainstreet Capital, we began this series to get us all more aware of our investment options and get us to a point of financial freedom.
Today, we will talk about Money Market fund.
A money market fund is also called a money market mutual fund. It is an open-ended mutual fund that invests in short-term, low risk debt vehicles like Treasury Bills, Bank Placements and Commercial Paper. Money market funds are managed with the goal of maintaining a highly stable asset value through liquid investments, while paying income to investors in the form of dividends. In addition, the money market often generates a low single-digit return for investors, which in a down market can still be quite attractive.
It is important to note that the investment minimum are lower than other investment types so barrier-to-entry is low.
Money Market funds are not insured against loss and actual losses are rare.
Unlike certain funds, Money Market Funds don’t generally invest in securities that trade small volumes or few buyers. They mostly trade in securities that are in fairly high demand (such as T-bills). This means they tend to be more liquid and as a result, investors can buy and sell them with comparative ease.
Because of how unstable the stock market can be, Money Market funds are relatively safe places to park money in spite of the single digit returns.
Potentially, inflation can hamper value of investments over time
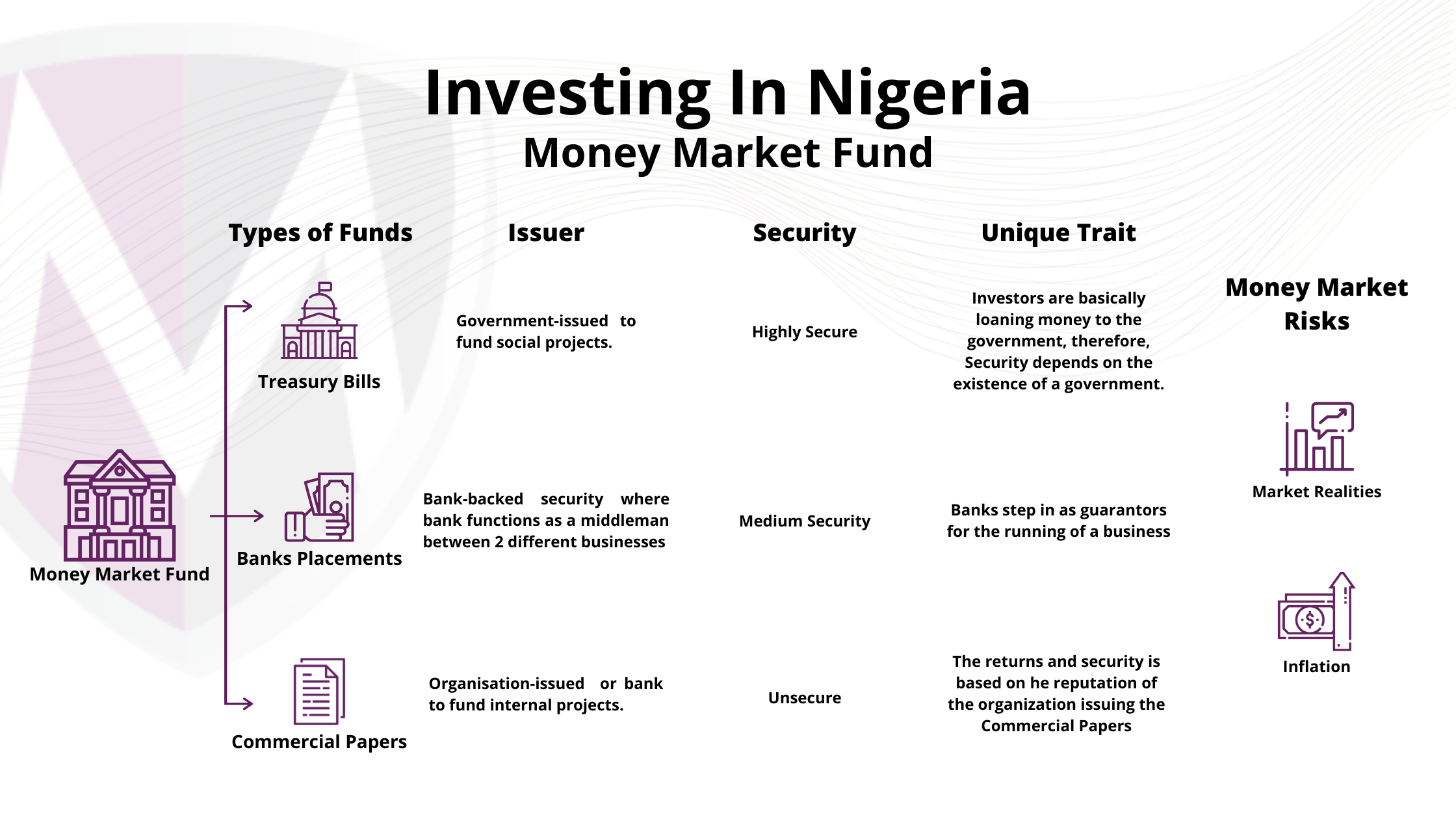
There are numerous Money Market instruments like Commercial Papers, Treasury Bills and Placements (private placements, bank placements), Bankers Acceptances and Certificate of Deposit
Basically, an issuer needs funds and takes a debt by issuing a specific amount of notes and the public buys these notes. The company proceeds to repay the investors with agreed interest at the appointed time.
Real life Example– General Electric wants to fund research on a new radiation machine and would need to raise capital for this venture. They could leverage their reputation as a long-standing profitable company and issue an unsecured debt instrument, such as commercial paper. They might make this choice as opposed to getting a line of credit from a bank after doing their numbers, and in the process, lower its cost of capital.
The longer the length of the investment, the higher the returns.
The returns are lower that most investments because of how secure it is.
T-bills compete with Inflation in that the if the inflation rates are higher than returns on T-bills, the investors lose and it becomes uneconomical to invest in T-bills. The effect is that there is less demand for T-bills and the prices drop.
The importer request goods from the exporter and the bank steps in as a guarantor for the importer. For the company that issues it, a banker’s acceptance is a way to pay for a purchase without borrowing to do so. For the company that receives it, the bill is a guaranteed form of payment.
This is dependent on market realities, demand and supply and the economy’s health.
As of May, 2020, Treasury bills returns was 1.90%. For Savings Deposits, the interest changes depending on the duration of the investment. For 1 month, 3.33%, for 3 months, 4.7% and 6 months, 4.98%.
How can you get it?
You can sign up with a commercial bank or talk to the Asset Management Team here at Mainstreet Capital. Also, you can open an account with us here.
This series has covered 4 topics- Stocks, Bonds, Mutual Funds and Money Market funds